Rob Donahue used to ride horses. He was a modern-day cowboy until he was stricken with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Now his muscles are weak. He can’t ride horses anymore. And his condition is worsening quickly. ALS will degenerate Donahue’s neurons and nervous system, and he will probably die in less than five years.
Another ALS sufferer, Nick Grillo, is trying to change all that. He’s put together a petition on Change.org to urge the FDA to fast-track approval of a new drug, GM-604, that would help people like Donahue and others like him.
“People can’t wait five, ten, 15 years for the clinical trial process,” said Grillo. “Things need to happen much quicker.”
But ALS is just one illness, and GM-604 is just one medicine. There are thousands of Americans suffering — many with terminal illnesses — while waiting on the FDA approval process.
Paradigm change
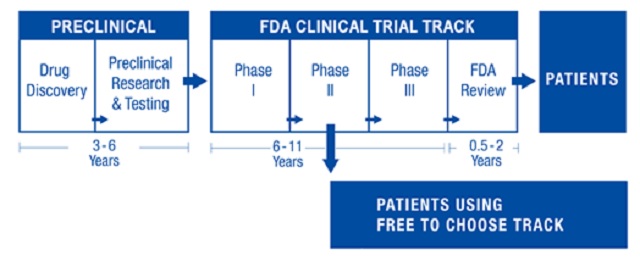
A paradigm change is essential because FDA culture has led to a situation where it costs an average of $1.5 billion and 12 or more years of clinical testing to bring a new drug to market. Medical innovation cannot thrive when only very large firms can afford to research and develop new drugs.
Another problem is that the FDA’s first goal is not to maximize innovation, but to minimize the chances that an FDA-approved drug leads to unanticipated adverse side effects and negative publicity. In particular, the FDA’s efficacy testing requirements have resulted in an ever-increasing load of money and time on drug developers. We can’t count on FDA bureaucrats to fix the broken system they created.
Even Congress, whose cottage industry is to regulate, admits that the current FDA system is a roadblock to fast-paced innovation. Congress’s own 21st Century Cures Initiative has led to many good ideas for delivering medical treatments, but even if successful, these ideas would bring only incremental improvements.
Americans deserve a bold plan to achieve genuine large-scale change enabling us to live longer, healthier, and more productive lives. And most importantly, we need a mechanism for allowing patients to exercise choice consistent with their own preferences for risk.
Congressional hearings: the missing seat at the table
The missing seat at the table is for someone who represents freedom — that is, the right of patients, advised by their doctors, to make informed decisions as to the use of not-yet-FDA-approved drugs.
Freedom in response to suffering and subjugation is a powerful rallying call. The Women’s Right to Vote constitutional amendment in 1920 and the Civil Rights Act of 1964 were not about incremental improvements; each was a paradigm change that brought forth a different and better future.
Absent from the congressional hearings over health care, however, has been a freedom agenda, specifically one designed to eliminate the FDA’s monopoly on access to new drugs.
Venture capitalists, where have you gone?
We hear very little about those who suffer and die because they were not able to access drugs stuck in the FDA’s testing pipeline, or about drugs that were never brought to market because FDA procedures made the development costs too high. There is an invisible graveyard filled with people who have died because of drug lag and drug loss.
The FDA’s deadly over-caution is why venture capitalists shy away from investing in biopharmaceutical startup firms. Venture capitalists are willing to take big risks on ideas that may fail. But failure due to regulatory risk is just too big a hurdle to overcome. Capital providers have other opportunities, even if those opportunities don’t involve cures for disease.
High costs and slow innovation are the hallmark of a monopoly. And, as medical science continues its rapid pace of innovation, the cost of lost opportunities for better health will increase even faster. The solution is to introduce consumer choice and competition.
Free to choose medicine
Three self-reinforcing principles are needed to bring rapid innovation to the biopharmaceutical marketplace.
First, we need a free-to-choose track that operates independently of the FDA and runs alongside the conventional FDA clinical testing track — a competitive alternative. After a new drug has successfully passed safety trials and shows initial effectiveness in early clinical trials, a drug developer could request that the drug be available for sale. Such an arrangement would allow for new drugs to be available up to seven years earlier than waiting for a final FDA approval decision.
Second, free-to-choose treatment results, including patients’ genetic data, would be posted on an open-access database. Patients and their physicians would be able to make informed decisions about the use of approved drugs versus not-yet-approved drugs. The resulting treasure trove of observational data would reveal, in real time on the Internet, which subsets of patients do extremely well or poorly using a particular new drug. This broad population of users — in contrast to the tight similarity of clinical trial patients — would better inform the biopharmaceutical industry, yielding better R&D decisions and faster innovation.
Third, some drug developers would want to provide free-to-choose drugs in order to quickly demonstrate that their drugs were effective, thereby enhancing the ability to raise needed capital. For patients who need insurance reimbursement and for developers seeking formal FDA recognition of their drugs’ safety and effectiveness, another kind of incentive is needed. That is, FDA observational approval would be based on treatment results reflected in observational data posted on the open-access Internet database.
In the foreword to my 2012 book, Free to Choose Medicine: Better Drugs Sooner at Lower Cost, Nobel Laureate economist Vernon Smith wrote, “These three design components for patient/doctor control of medical treatment are both innovative and soundly based. With this conceptual blueprint, legislation could be crafted to promote both expanded consumer choice and the discipline of choice to the long-term benefit of society.”
Opposition
FDA proponents would bolster the fear that “unsafe” drugs could flood the marketplace. But the FDA cannot define what is “safe.” Only patients with their unique health conditions, treatment profiles, and preferences for taking risk can define what is safe for them. That is what freedom is all about: individual choice. Keep in mind that the likely large number of free-to-choose patients with widely varying health conditions would yield uniquely useful safety data superior to safety readouts from clinical trial data.
The free-to-choose medicine plan is voluntary and would not disturb those who want to use only approved drugs. A reasonable implementation schedule would first allow the new system to be used by patients fighting a life-threatening illness, as they are the ones most in need of access to the latest drug advancements.
Biopharmaceutical firms likely to oppose such a plan would include larger firms who consider their expertise in dealing with the FDA bureaucracy as an especially valued competitive advantage over their smaller competitors. We should expect support from firms with a high level of scientific skill, but limited skill and resources in dealing with FDA bureaucracy. Nevertheless, even those firms initially opposed should question their current business models, which produce sky-high prescription drug prices and the very real chance that government at some future point will impose price controls. Why not set into motion an alternative that can lead to radically lower development and approval costs with concomitant lower prescription drug prices while maintaining industry profitability levels?
Trial lawyer organizations will be expected to contribute mightily to defeat any freedom-based legislation. They do not want Americans legally taking personal responsibility by way of voluntary contracts, even if there are life-saving benefits to be had.
Patients are the ultimate beneficiaries of competition, and they are a powerful force for those who want a fundamental restructuring of the FDA. Right-to-try state laws are designed to allow those dealing with life-threatening illnesses access to not-yet-approved drugs. These laws’ enormous popularity indicates that a well-run campaign could generate similar support at the federal level for free-to-choose medicine.
Freedom should be part of the national debate on 21st century medical legislation. For that to happen, we need to give freedom lovers and chronic sufferers a seat at the table.
Every American should have the right to make informed decisions that can improve health or save lives. Freedom is not something to fear; it is the best route forward to a more innovative, efficient, and humane medical system.
 Gennady Stolyarov II
Gennady Stolyarov II