“The Line” for Green Cards Is So Long, You Might Die of Old Age Waiting – Article by David Bier

Immigrants are often told to “get in line” if they want to stay in the United States. This demand is disingenuous for many reasons. Many immigrants have no line to get into. And even if they do, we are telling them to join these lines when no one even knows how long they are. In many cases, we could be asking immigrants to join a line that they will literally never live to see the end of.
Immigrants might face a line they will literally never live to see the end of. We don’t know much about who’s in these lines until they get to the front, but here’s what we do: Thousands of immigrants come to the United States each year on temporary work visas. While working in temporary status, some of their employers petition on their behalf to obtain green cards for them to stay permanently. If the employer has jumped through all the appropriate hoops, the worker can then apply for a visa, if — and this is a big if — the limit on visas that year has not been reached.
This is where the line — and the waiting — starts. For lawmakers trying to fix the immigration system, figuring out how many people are at this point in the process is critical. But even they don’t know.
5 million people are waiting abroad.We do have a good idea how many people are waiting overseas. The State Department keeps track of those numbers and publishes them annually, and we’re quickly approaching 5 million immigrants waiting abroad, which is an astounding number on its own.
But for temporary immigrants already in the United States, the Department of Homeland Security doesn’t keep track — or doesn’t publish — the number of applicants who are prevented from receiving a green card due to the limits.
The State Department publishes a monthly visa bulletin that tells people in either line — here or abroad — whether they can apply for a green card. It lists a date, as seen below, next to a visa category. This date is the cutoff. If your employer’s petition was filed after the date listed, you cannot apply for a green card yet.
Figure 1: Visa Bulletin — Application Final Action Dates for Employment-Based Preferences Source: State Department
Source: State Department
These dates can sometimes create the misleading impression that immigrants from India, for example, will have “only” twelve years to wait for a green card. But that’s not right. That’s just how long immigrants who are currently receiving their green cards today have been waiting. We simply don’t know how many people applied since October 2004, so we don’t know how long someone applying today will have to wait.
Even the State Department doesn’t know who’s in line.Apparently, even the State Department doesn’t know who is in the line. When the department moves up the dates, it basically guesses how many people applied between the current date and the new date. When it moved the dates up for EB-2 and EB-3 categories from India (workers who have a Master’s or a Bachelor’s degree) to 2010 and 2007, the government was flooded with more applications than there were visas available, and so it moved the dates back again to 2004.
This mistake, however, gave us some small insight into who is waiting.
We cannot know for sure whether everyone who could apply submitted an application before the date moved back, but the Department of Homeland Security lists 46,098 Indians currently waiting at this stage. The State Department also lists almost 30,000 more waiting for employment-based green cards abroad, for a grand total of nearly 76,000 Indians. Because each country is limited to no more than 2,800 visas in each category, clearing just this backlog alone will take almost 10 years for EB-2 and more than 14 years for EB-3.
But that only gets us up to 2007 and 2010 for those categories. We simply have no idea how many people could be waiting beyond those dates. It would be nice to be able to estimate the number based on green card applications filed before those dates, but the list only gives us the number pending at any given time. It doesn’t show the total number submitted in a year. Some may have already been processed. Others may have been submitted later, after other older applications passed through.
A rough estimate shows 230,000 people in line, a fifty year wait.We know that in 2008, there were at least 19,512 green card applications under EB-2. For EB-3, the numbers haven’t gotten up to 2008 yet, but in 2006, there were at least 12,708 filed for that category. Simply carrying these numbers forward for each unknown year, there would be roughly 230,000 people in line, which would translate into an almost 50-year wait.
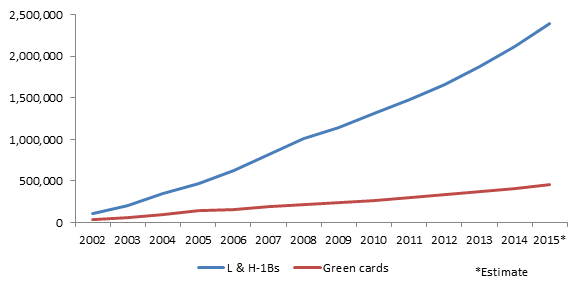
The situation is likely worse than that. We know that the number of Indian temporary workers has increased dramatically relative to the number of green cards issued to them in the past couple decades (Figure 2). We also know that roughly half of all employment-based labor certifications (the step employers complete prior to submitting most EB-2 and EB-3 green card petitions) are for Indian workers.
Figure 2: Total Cumulative Green Cards and L or H-1B Visas Issued to Indians Since 2007
 Sources: H-1B/Ls: USCIS/State Department; Green cards: DHS
Sources: H-1B/Ls: USCIS/State Department; Green cards: DHS
Since 2002, 450,000 Indians received a green card, while roughly 2.4 million high-skilled immigrants from India and their families have entered under the H visa or L visa (for employees transferring to a U.S. branch of their company). Some portion of these workers could have been beneficiaries of an EB-3 green card petition after 2007, the last date on which we know anything about who is in line.
They’ll be waiting somewhere between 50 and 350 years. All we know is this: somewhere between 230,000 and 2 million Indian workers are in the backlog, so they’ll be waiting somewhere between half a century and three and a half centuries. It is entirely possible that many of these workers will be dead before they receive their green cards. And that’s just one country. The backlogs for Chinese immigrants and immigrants from the Philippines continue to grow as well.
America’s immigration system is broken worse than anyone can even know.
David Bier is an immigration policy analyst at the Cato Institute’s Center for Global Liberty and Prosperity.
This article was originally published on FEE.org. Read the original article.

